This week we look at what happens with multidimensional and associative arrays. As you look at these you will start to understand where you can use JavaScript when building your Web sites.
Multidimensional Arrays
This type of an array is similar to parallel arrays. In a multidimensional array, instead of creating two or more arrays in tandem as we did with the parallel array, we create an array with several levels or “dimensions.” Remember our example of a spreadsheet with rows and columns? This time, however, we have a couple more columns.

Multidimensional arrays can be created in different ways. Let’s look at one of these method. First, we create the main array, which is similar to what we did with previous arrays.
var emailList = new Array();
Next, we create arrays for elements of the main array:
emailList[0] = new Array("President", "Paul Smith", "[email protected]");
emailList[1] = new Array("Vice President", "Laura Stevens", "[email protected]");
emailList[2] = new Array("General Manager", "Mary Larsen", "[email protected]");
emailList[3] = new Array("Sales Manager", "Bob Lark", "[email protected]");
In this script we created “sub arrays” or arrays from another level or “dimension.” We used the name of the main array and gave it an index number (e.g., emailList[0]). Then we created a new instance of an array and gave it a value with three elements.
In order to access a single element, we need to use a double reference. For example, to get the e-mail address for the Vice President in our example above, access the third element “[2]” of the second element “[1]” of the array named emailList.
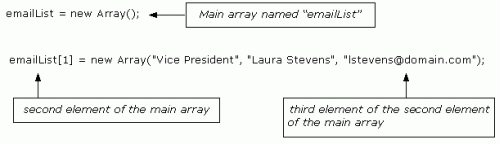
It would be written like this:
var vpEmail = emailList[1][2]
alert("The address is: "+ vpEmail)
|
You could also retrieve the information using something like:
var title = emailList[1][0]
var email = emailList[1][2]
alert("The e-mail address for the " + title +" is: " + email)